SK channels enhancing excitability are expressed at or near the
Download scientific diagram | SK channels enhancing excitability are expressed at or near the soma of CA1 pyramidal cells. A, Representative experiment showing the effects of D-TC (100 M) applied in the aCSF on the firing of an XE991-treated neuron. In aCSF containing 10 M XE991, the neuron fired a burst of four spikes (a), which was increased to seven spikes by D-TC (b) in a reversible manner (c). B, C, Bar histogramssummarizingtheeffectofD-TCappliedintheaCSFonthenumberofintraburstspikesandDSs,respectively(n5).D,SchemeofahippocampalsliceshowingpointsoffocalD-TCapplications(1-4) in relation to the recording point (3). E, Data from a representative experiment in which D-TC was focally applied to distal (1), proximal apical dendritic (2), and somatic regions (3) of the recorded neuron. The neuron was superfused with aCSF containing 10 M XE991. The graph depicts the number of intraburst spikes at each time point. F, Selected recordings from the experiment described in E. The letters depict the time points at which the recordings were obtained (triangles in E). Note extra spikes in c and e. G, Data from a representative experiment in which D-TC was focally applied to basal dendritic (4) and somatic regions (3) of the recorded neuron. Otherwise, similar to E. H, Selected recordings from the experiment described in G. Note extra spikes only in c. I, Bar histogram summarizing the number of intraburst spikes generated by XE991-treated neurons 5 min after focally applying D-TC to soma (n 7), proximal apical dendrites (n 7), distal dendrites (n 6), and basal dendrites (n 4). The number of neurons in the control group was seven. Significant increase was achieved only when D-TC was applied to the soma or to the proximal dendrites. from publication: Role of Small Conductance Ca2(+)-Activated K+ Channels in Controlling CA1 Pyramidal Cell Excitability | Small-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (SK or KCa2) channels are widely expressed in the CNS. In several types of neurons, these channels were shown to become activated during repetitive firing, causing early spike frequency adaptation. In CA1 pyramidal cells, SK channels in | Pyramidal Cells, Hippocampus and Neuron | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Presence of Small-Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium (SK) Channels in the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems and Their Role in Health and Disease

Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel - an overview

N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors mediate activity-dependent down-regulation of potassium channel genes during the expression of homeostatic intrinsic plasticity, Molecular Brain
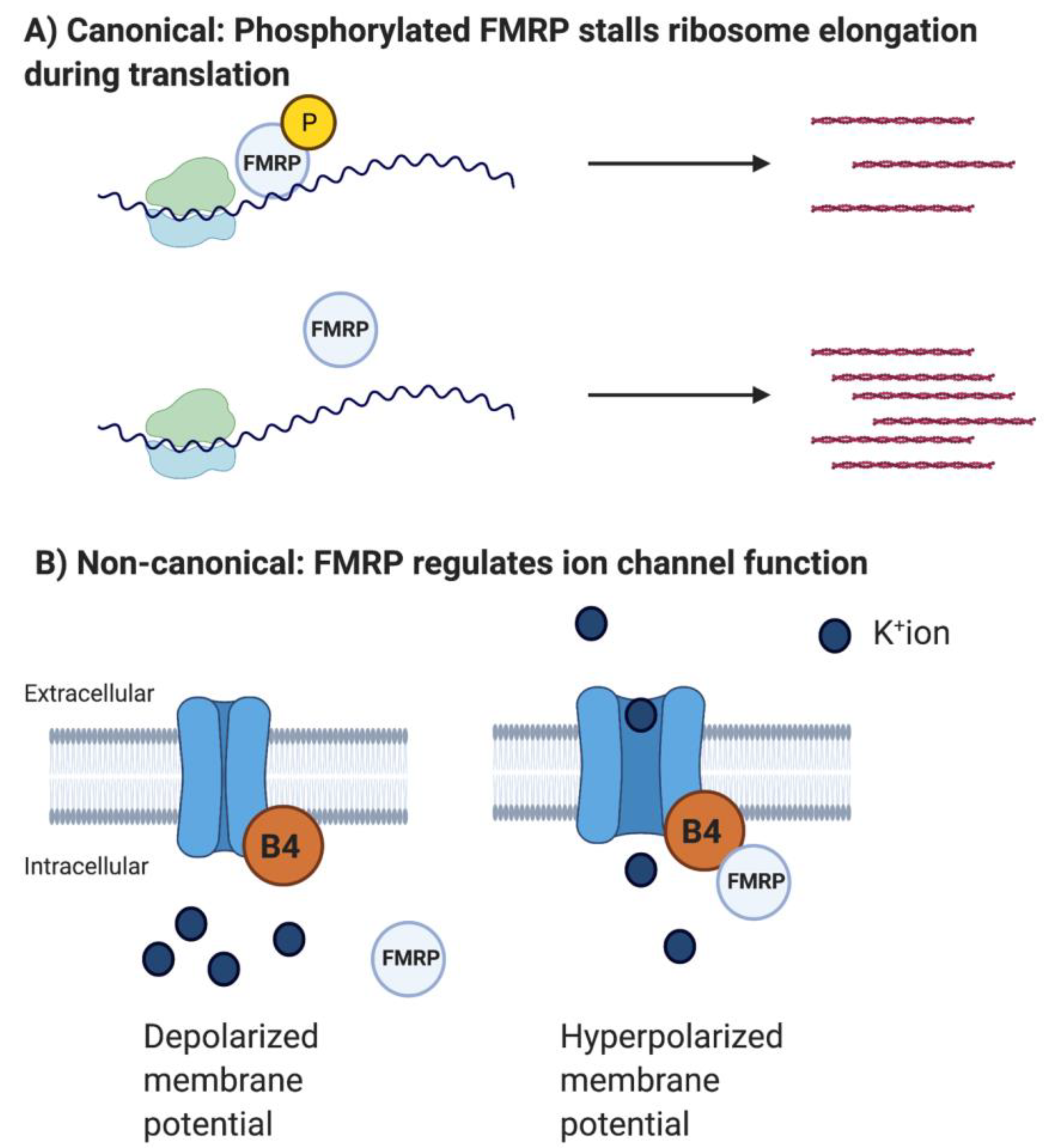
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Resting Membrane Potential - FasterCapital
SK Channels and Heart Disease
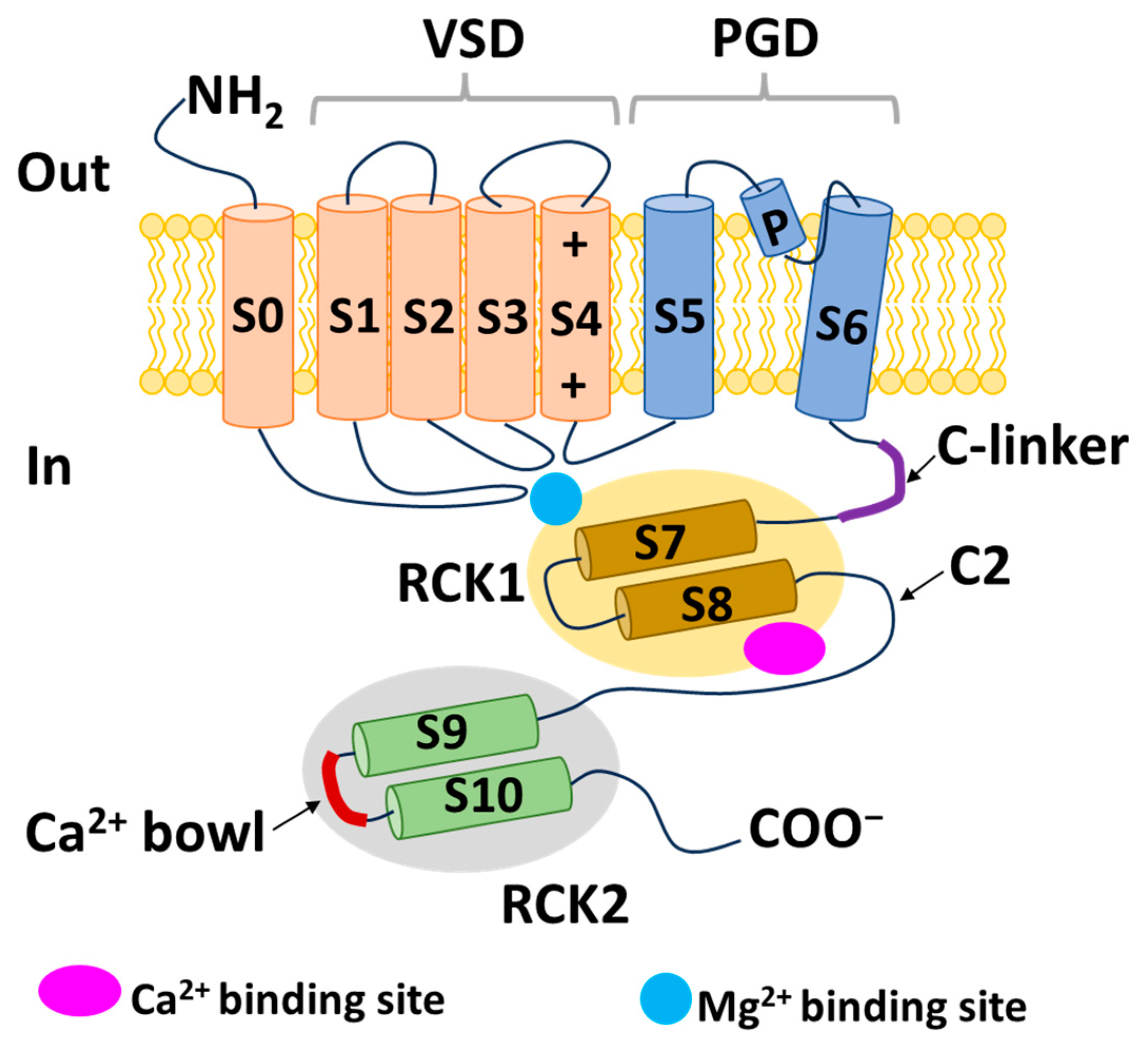
IJMS, Free Full-Text

SK Channels and Heart Disease
BJDVD

SK2 channel regulation of neuronal excitability, synaptic transmission, and brain rhythmic activity in health and diseases - ScienceDirect
Functional localization of SK channels in CA1 pyramidal cells. A

PDF) Role of Small Conductance Ca2(+)-Activated K+ Channels in

SK Channel - an overview









