Effect of permeability on cooling of a magmatic intrusion in a geothermal reservoir - UNT Digital Library
Numerical modeling of the transient cooling of a magmatic intrusion is described in a geothermal reservoir that results from conduction and convection, considering the effects of overlying cap rock and differing horizontal and vertical permeabilities of the reservoir. These results are compared with data from Salton Sea Geothermal Field (SSGF). Multiple layers of convection cells are observed when horizontal permeability is much larger than vertical permeability. The sharp drop-off of surface heat flow experimentally observed at SSGF is consistent with the numerical results. The age of the intrusive body at SSGF is estimated to be between 6000 and 20,000 years.
Effect of permeability on cooling of a magmatic intrusion in a geothermal reservoir - UNT Digital Library

PDF) Quantifying the stress distribution at the Rotokawa Geothermal Field, New Zealand
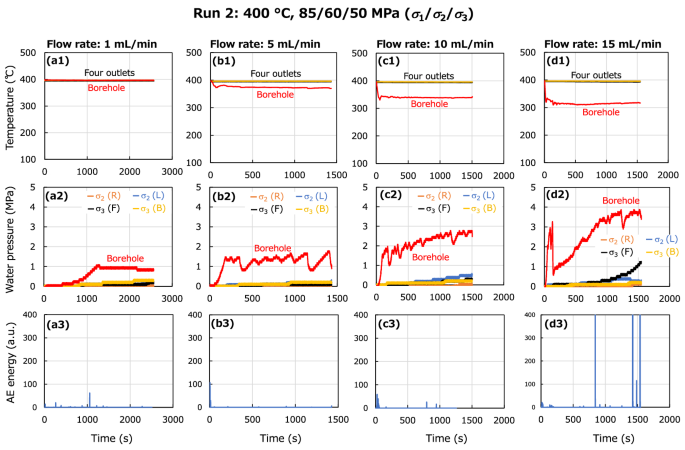
Cooling-induced permeability enhancement for networks of microfractures in superhot geothermal environments, Geothermal Energy

An up-to-date perspective of geothermal power technology - ScienceDirect
Effect of permeability on cooling of a magmatic intrusion in a geothermal reservoir - UNT Digital Library
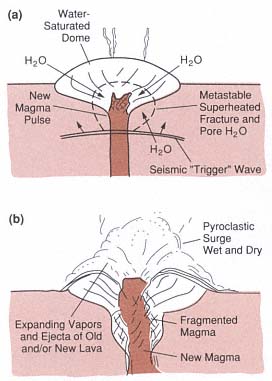
Volcanology and Geothermal Energy

Simulation of cooling in a magma chamber: Implications for geothermal fields of southern Peru - ScienceDirect

PDF) Interpretation of Recent Unrest Events (Bradyseism) at Campi Flegrei, Napoli (Italy): Comparison of Models Based on Cyclical Hydrothermal Events versus Shallow Magmatic Intrusive Events

A simplified geothermal model showing schematically a reservoir at

The geothermal magmatic system at the northern Rahat volcanic field, Saudi Arabia, revealed from 3D magnetotelluric inversion - ScienceDirect